How is manic depression or bipolar disorder diagnosed and treated?
How often have you witnessed your immediate manager’s mood change from a high to a low, causing you to question whether or not he is a maniac? There is a strong possibility that he is suffering from manic depression, which is also referred to as Bipolar depression. It is called bipolar depression because the patient’s mood lurches erratically between two extremes of what would be considered normal conduct (high and low). The condition known as manic depression, often called bipolar depression, is a kind of depression that affects people of all ages and can affect both men and women.
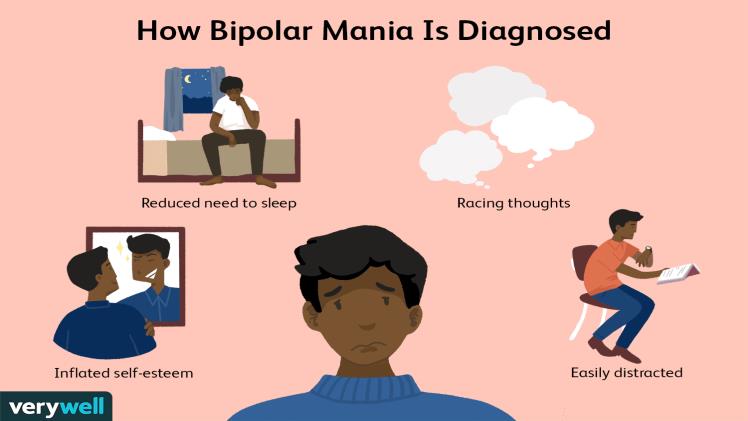
Manic depression or bipolar disorder is diagnosed in the light of the following points:
Manic Episode
If an elevated mood persists throughout the day alongside a number of other symptoms, the individual is said to be experiencing a manic episode, which is a state of manic attacks. It would be necessary to observe this individual for longer than three to four days with regard to these symptoms. For a person to be diagnosed with the irritable mood subtype of psychotic depression, there must be four additional symptoms present in addition to the irritable mood. Click here for more about Deloitte
Depressive Episode
When an individual’s mood is at an all-time low for the majority of one full week to two weeks, the individual is said to be experiencing a depressive episode. In order for a person to be diagnosed with this form of bipolar illness, they will often need to exhibit at least five of the associated symptoms.
Mixed Bipolar Episode
There have been a lot of examples in which the individual seems extraordinarily down and depressed at times, but then, just when you believe he is a manic-depressive type of person, he suddenly springs back to life and exhibits extremely high levels of energy. People who exhibit these symptoms are said to be suffering from the mixed bipolar episode.
More Info About BMW X6
Bipolar depression is treated with the following steps:
Medication
In situations like these, medical professionals typically advise patients to take mood stabilizers, a category of medication that is designed to address the symptoms of manic depression. Antidepressant medication is favored by doctors as a treatment option for their patients because of the role it plays in mitigating the highs and lows associated with mood swings.
Monitor the Thyroid
Huge swings in mood is often attributed to abnormal thyroid function. An individual must hence be required to keep a close watch on the functioning of his thyroid gland by regular tests to ensure that he is not a victim of irregular mood swings.
Spot Relapses
The greatest person to treat manic depression is frequently the person who also suffers from the condition. This can be accomplished by the individual recognizing patterns in his behavior, particularly relapses, which will enable him to successfully combat the mood swings that he experiences.
The individuals suffering from manic depression, as well as the caregivers and family members of the sufferer, are all affected by the condition. In addition to making the individual unpredictable in the context of society, it undermines the credibility of the members of his family. It is possible to treat manic depression by adhering to a few straightforward stages of both medical treatment and self-observation.




